In the world of web traffic and servers, ensuring that your website remains available and performs efficiently is crucial. One of the key tools to make this possible is a load balancer. Let’s understand what a load balancer is, how it works, and see some examples with a detailed flow chart.
What is a Load Balancer?
A load balancer is a device or software that efficiently distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers. This distribution ensures no single server becomes overwhelmed, which can lead to downtime or slow performance.
How Does a Load Balancer Work?
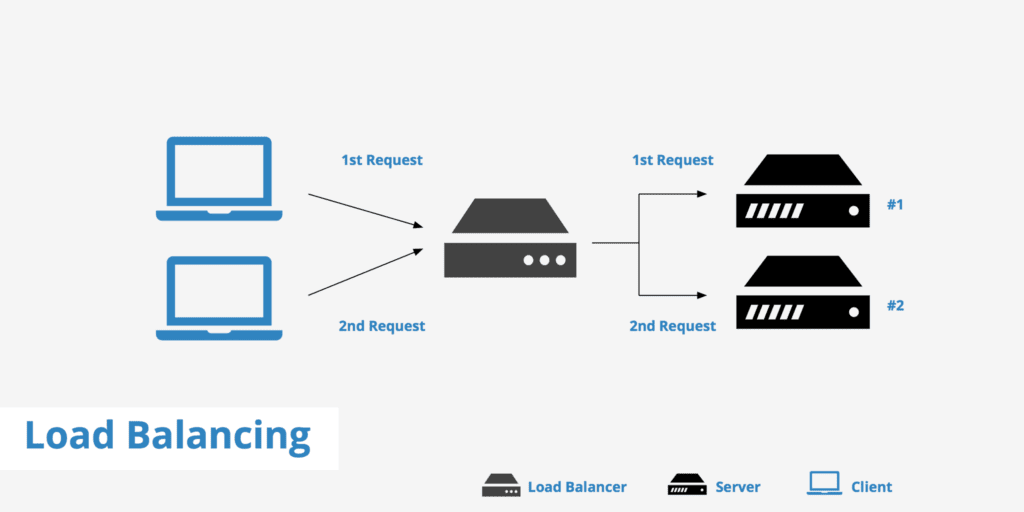
Think of a load balancer as a traffic cop stationed in front of your web servers. It directs incoming requests to different servers based on various algorithms. Here’s a breakdown of how it generally works:
1. Incoming Traffic: When users send requests to a website, these requests first go to the load balancer.
2. Server Selection: The load balancer uses a specific algorithm to decide which server should handle each request.
3. Forwarding Requests: The chosen server processes the request and sends the response back to the load balancer.
4. Response Delivery: Finally, the load balancer forwards the server’s response back to the user.
Types of Load Balancing Algorithms
There are several algorithms that a load balancer can use to distribute traffic:
1. Round Robin: Requests are distributed evenly across all servers in a circular order.
– Use Case: Useful for evenly distributed workloads.
– Pros: Simple and easy to implement.
– Cons: Doesn’t account for server load or capacity.
2. Least Connections: Requests are sent to the server with the fewest active connections.
– Use Case: Ideal for environments where sessions or requests can vary in length.
– Pros: Balances based on current load.
– Cons: More complex to implement than Round Robin.
3. IP Hash: The client’s IP address is used to determine which server will handle the request.
– Use Case: Useful for maintaining session persistence.
– Pros: Ensures a client is consistently directed to the same server.
– Cons: Can lead to uneven load distribution.
Example of Load Balancing
Imagine a website that gets 1000 requests per second. Without a load balancer, a single server would have to handle all these requests, leading to delays or crashes. With a load balancer, those 1000 requests could be evenly distributed across five servers – each handling 200 requests per second.
Real-World Scenarios
– E-commerce Sites: During sales events, traffic spikes are common. Load balancers ensure that all requests are managed efficiently without crashing the site.
– Cloud Services: Platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud use load balancers extensively to manage resources and ensure high availability.
– Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute web content across multiple servers worldwide, with load balancers managing which server delivers content to a user based on location, load, and other factors.
Below is a more detailed diagram to depict how a load balancer operates:
Key Benefits of Load Balancers
1. Increased Reliability: By distributing traffic across multiple servers, load balancers help prevent downtime.
2. Improved Performance: Load balancers ensure that no single server becomes a bottleneck, improving response times for users.
3. Scalability: New servers can be easily added to handle growing amounts of traffic without affecting user experience.
Conclusion
Load balancers play a crucial role in modern web infrastructure by ensuring reliability, performance, and scalability. Whether you are running a small personal blog or a large e-commerce site, implementing a load balancer can significantly enhance your website’s user experience.
